Data analytics in Internal Audit – when it makes sense
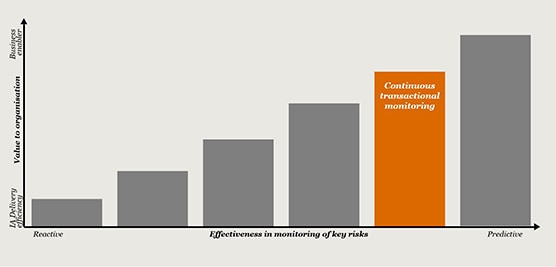
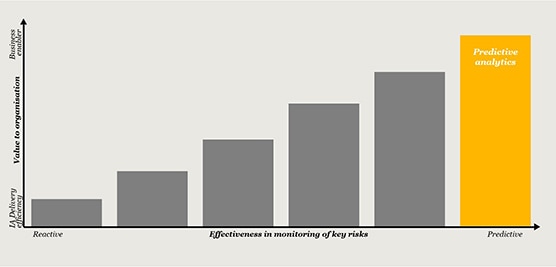
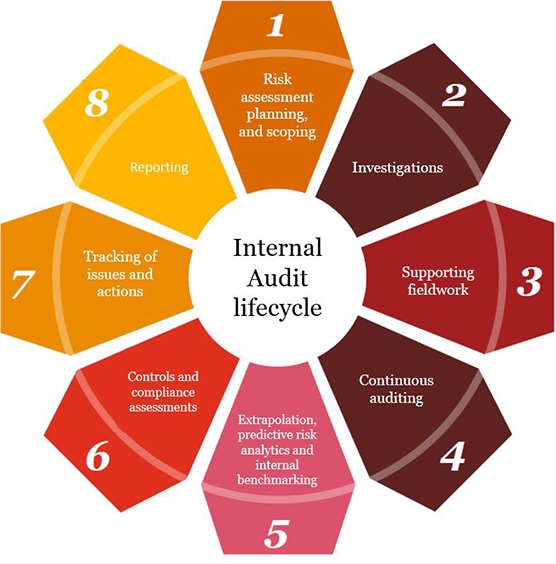
While data analytics has typically been used for data acquisition and fieldwork, we firmly believe that it can, and should, be harnessed across the entire Internal Audit lifecycle.
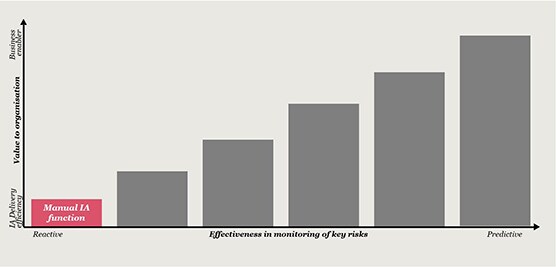
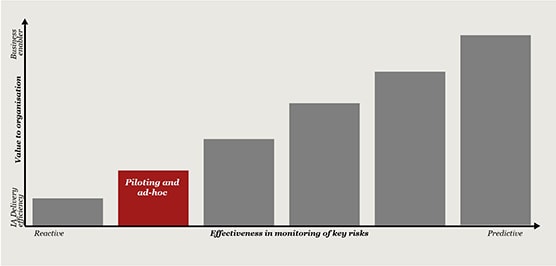
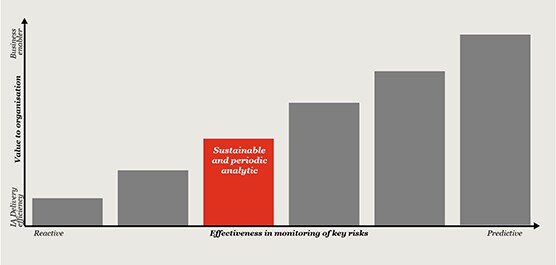
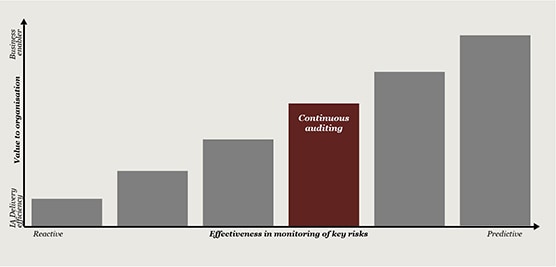
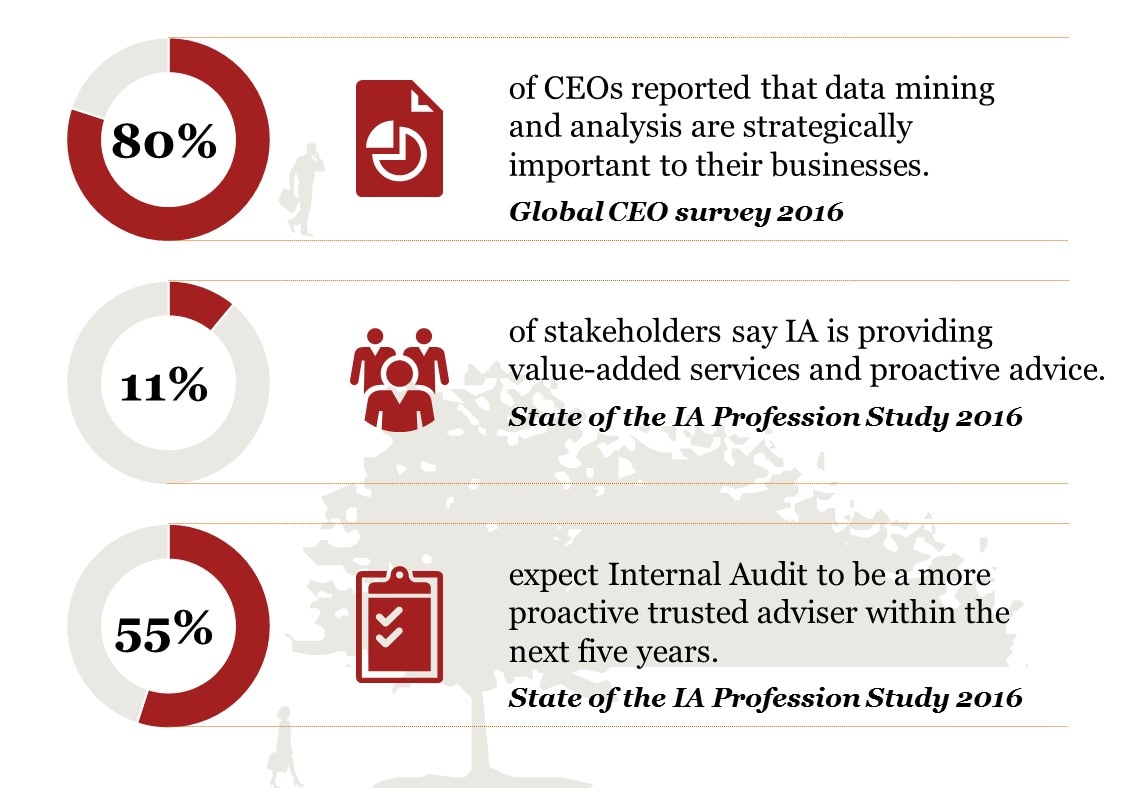
From our research and interactions with Heads of Internal Audit (HIAs) and Internal Audit (IA) stakeholders, we have found that leading functions have moved beyond computer assisted audit techniques (CAATS) and are designing and deploying data analytics across their entire audit life cycle, leveraging the latest generation of data analysis and reporting tools. This is enabling a sharper focus on risk areas and business issues, as well as generating efficiencies throughout the audit process.
The path to effectively harnessing data analytics is not easy, and even leading functions can experience resistance along the way. Challenges around data acquisition, identifying the right internal and external resources to support, and agreeing which technology is fit for purpose are commonplace. It might not also be feasible to deploy across the entire lifecycle at first but it should be the end goal.