Ten tips to manage commodity risk for competitive advantage
Download: Actively managing commodity risk for competitive advantage
Commodity risk is emerging as a critical differentiator of business performance, driven by a number of key trends including commodity price volatility and an increase in the complexity of commodity markets.
- This price volatility and market complexity is the ‘new normal’ and has major implications for business performance.
- We see users of commodities especially within retail and consumer and industrial products being more active in their management of risk but note there is still a significant journey for most companies if they want to create capability which is able to add value to the business.
- As companies look to improve their CRM capability it is imperative to align all stakeholders across Finance, Treasury and Procurement given the potential divergence of objectives these functions will have.
At a recent dinner we hosted for directors of procurement and risk in retail and beverage companies we debated what an appropriate strategy should be and what are the lessons learnt as companies begin to build and implement commodity risk management capability. Everyone acknowledged that this as a significant, and evolving risk for companies which need to manage to mitigate risk or in some cases maximise it, so they can potentially lower procurement costs. We have set out below the key points clients raised.
Please take a look at the discussion outline attached below for further context.
- Risk approach for strategic advantage
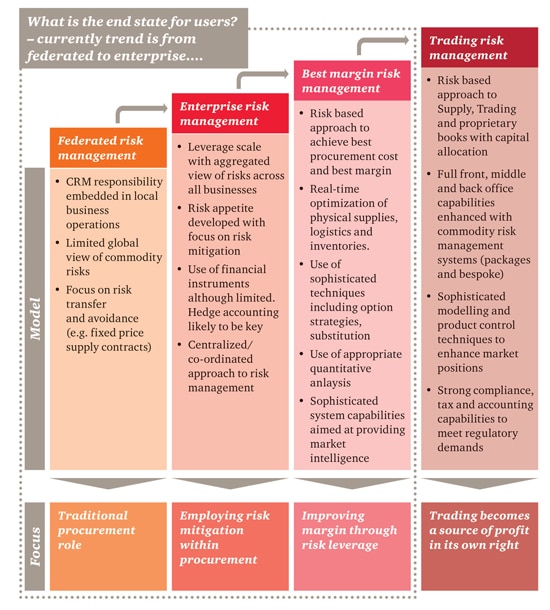
As a source of strategic advantage, procurement functions are actively considering or adding a risk based approach to the traditional functions. This is a step change from viewing risk management mainly in a control context - The PwC risk maturity procurement framework
Clients found the PwC risk maturity framework for procurement activities useful in articulating their current and future end states. The four main states comprise;- Federated risk management : a traditional procurement role with a focus on risk transference and avoidance; often at a divisional level
- Enterprise risk management: employing risk mitigation (including hedging) in a more centralised approach
- Best margin risk management: seeking to further enhance margins though risk leverage by trading around areas of comparative advantage
- Trading risk management: taking risk leverage further by also seeking profit from trading in its own right instead of through margin enhancement alone
- Complexity in the market
As the commodity derivatives market became more liquid, other investors outside of those supplying and purchasing physical commodities were becoming involved in the supply chain. This was contributing to price volatility and impacting business performance - Identifying the exposure
In purchase contracts, a number of companies indicated the challenges of determining the ‘indirect’ commodity exposure especially if purchasing finished goods. So, it’s difficult to identify the exposure to commodity prices making it harder to accurately manage that risk - Organisational responsibility
The responsibility of managing commodity risk often sits within Procurement although Treasury increasingly play a role in strategy and execution. Participants highlighted it At times it is challenge to get stakeholder alignment between these two and other related functions) - External stakeholder alignment
The involvement of the ExCo and Board in this process is critical in developing a risk based approach to procurement because of the need for alignment across both internal and external stakeholders and the potential impact on the shareholder value proposition. - Risk analytics
Some are exploring using risk analytics such as Cash Flow at Risk and Earning at Risk to better model the impact of commodity price movements. If risk analytics are to be used then it is important to be able to explain the outputs to those that are going to be reviewing them. It was recognised that risk analytics has its limitations in using historical data. - Accounting
When managing commodity price risk the majority felt it was important to take into consideration the accounting implications. It was recognised that the implementation of new accounting standards (IFRS 9) should help achieve hedge accounting for commodity price risk - Team
To appropriately manage commodity risk, existing category management skills needed to be supplemented with financial risk management and commodity market expertise - Systems
There is no end to end system that has the capability to assist with managing commodity risk as well as the other risks that Treasury are have to manage. It was recognised that TMS vendors are developing their commodity risk management offering however it was believed that this would need to be whilst working alongside a corporate.
In addition, there are configurable commodities trading and risk management systems in the market however there are still likely to be significant development, implementation and ongoing maintenance costs to cover specific aspects of procurement